HCS Technology Group has developed the following Wireless Network best practices and recommendations to better the end user experience through technological steps. The document will serve as a useful reference for technical staff as well.
- Focus on 5GHz channels.
- Avoid using 2.4GHz channels. If 2.4GHz channels are required use channels: 1/6/11 ONLY.
- Reduce the Radio Transmit Power (TX) to minimal levels as 2.4GHz has tremendous range.
- 2.4GHz channels are pervasive and will cover a wider area than expected.
- If 2.4GHz channels are required, set the 2.4GHz channels on every other Access Point (A/P) and common areas to reduce the amount of RF pollution.
- If 2.4GHz channels are required, the 2.4GHz channels should be set 10 dBm cooler than your hottest 5GHz.
- Reduce the Radio Transmit Power (TX) to lowest possible so that you achieve a -80 to -90 dBm with an active Access Point (A/P).
- Wi-Fi RSSI measuring -65dBm to -60dBm or better. Apple devices will not scan until their associated Access Point (A/P). RSSI drops below -70dBm.
- Wi-Fi RSSI measuring -65dBm to -60dBm or better. Apple devices will not scan until their associated Access Point (A/P). RSSI drops below -70dBm.
- Use 20 MHz wide channels for both 2.4GHz and 5GHz.
- Using 20 MHz wide channels and 5GHz gives you more channels for strategic mapping and reduces the chances of overlapping.
- If you require more bandwidth increase to 40MHz wide for 5GHz.
- This will reduce available channels.
- Proper channel mapping becomes critical.
- If you require more bandwidth increase to 40MHz wide for 5GHz.
- Use the full spectrum including Dynamic Frequency Selection (DFS) channels.
- Signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) should be 20 dB or better.
- Test for ground based radar channel changes at sites to see if you are in an at risk area.
- Note: that these hops can be triggered by some Access Point (A/P) own sensitivity to RF radiation and not from actual radar.
- Turn off any Printers that may be broadcasting a Wi-Fi setup (typically in the 2.4GHz spectrum).
- Be aware that cell phone Hot Spots broadcast in the 2.4GHz spectrum.
- Avoid using Hidden SSID’s (Service Set Identifier).
- Use Wi-Fi authentication security protocols to protect all SSID’s.
- Skip channels between adjacent Access Points (A/P).
- This provides an extra buffer between adjacent channels reducing the risk for overlap and co-channel interference (CCI).
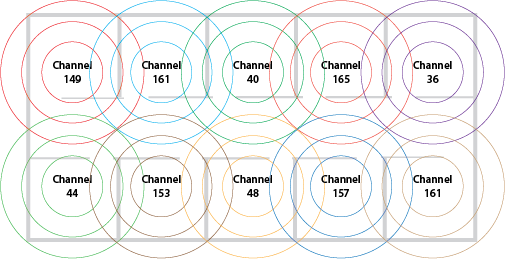
List of Wi-Fi recommendations:
- Decrease the total number of SSIDs that are being broadcasted by the Access Point (A/P).
- Use 20Mhz wide channels, which will allow for more unique 5GHz channels available on their Access Point (A/P).
- Use Dynamic Frequency Selection (DFS) Channels.
- Design for -65dBm cell edge for Primary SSID.
- Design for -65dBm cell edge for Secondary SSID.
- Scope Access Points (A/P) to have unique channels, and avoid channel overlapping in close proximity.
- Configure each Access Point (A/P) to not have the radios broadcast at 100% power (site survey will determine at what strength each Access Point (A/P) should be configured).
- Disable broadcasting on 5GHz 149 & 153) on Access Points (A/P) , to optimize peer-to-peer AirPlay from the Apple TVs, as documented here: https://help.apple.com/deployment/ios/#/apd8fc751f59.
- Strongly consider using 5GHz only for institution-owned devices (primary SSID).
- Strongly consider using 2.4GHz for Guest network SSID.
- Turn off any Printers that may be broadcasting a Wi-Fi setup (typically in the 2.4GHz spectrum).
- Be aware that cell phone Hot Spots broadcast in the 2.4GHz spectrum.
Cisco and Meraki specific suggestions for Apple Devices
- Set Minimum Data Rate to 12 Mbps.
- Enable 12 and 24 as Mandatory Rates.
- Design for signal-to-noise ratio of 25 dB or better.
- Keep Retry rates of less than 15%.
- Keep Layer 3 packet loss of less than 1%.
- Keep Jitter less than 100ms.
- Average Channel Utilization of less than 40% – target less than 30%.
- Turn on support for 802.11r – Fast Transition.
- Turn on support for 802.11k – Neighbor Reporting.
- Turn on support for 802.11v – BSS Transition Management.
- Apple devices will not scan until their associated Access Point’s (A/P) RSSI drops below -70dBm.
- Set WMM On.
- Set AVC on – set Voice QoS to Platinum.
Determine if the Wi-Fi infrastructure is configured for “client-to-client” communications
- Wi-Fi vendors have differing terminology for client-to-client communications, some examples include:
- Aerohive - Enable inter-station traffic
- Aruba - Deny InterUser Traffic
- Cisco - Peer-to-Peer Blocking
- Meraki - Bridge Mode
- Meru - Isolate wireless to wireless traffic
- Ruckus - Client Isolation
- Xirrus - Sta2Sta-Blocking
Apple TV and your Wireless network
Based on documented best practices, the following links provide Apple TV best practices with recommendations for Network design and implementation.
http://help.apple.com/deployment/ios/#/apd8fc751f59
https://support.apple.com/en-us/HT204291
https://support.apple.com/en-us/HT202618